Deployers have multiple metadata aggregates from which to choose. This page outlines available options. Policy considerations and general configuration issues are discussed on the Metadata Consumption page. Guidance on how to configure specific metadata clients Metadata Client Software is also available elsewhere in this wiki.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
A description of each metadata aggregate follows.
Metadata Aggregates
| Note |
|---|
All aggregates listed below are production-quality metadata aggregates. |
The InCommon Export Aggregate (which is not intended for end entities) is described in a separate wiki topic.
Metadata Aggregates
| Div | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
InCommon Operations distributes multiple production-quality On December 18, 2013, InCommon Operations will deploy three new metadata aggregates at the following permanent HTTP locations:
- http://md.incommon.org/InCommon/InCommon-metadata-preview.xml (productionpreview)
- http://md.incommon.org/InCommon/InCommon-metadata-fallback.xml (fallbackmain)
- http://md.incommon.org/InCommon/InCommon-metadata-previewfallback.xml (previewfallback)
The new locations will ultimately replace the current HTTP location of production metadata:and
- http://wayfmd.incommonfederationincommon.org/InCommon/InCommon-metadata-idp-only.xml (legacy)
Moving forward, all new metadata services will be deployed on vhost md.incommon.org. Legacy vhost wayf.incommonfederation.org will be phased out.
- IdP-only)
| Note |
|---|
You may also use TLS (https) to download the aggregates noted above. You are strongly advised not to depend solely on TLS for the security of your metadata downloads, and to continue the critical practice of verifying the signature on metadata according to the instructions on the Metadata Consumption page. Clients that are capable of doing so should continue to download metadata over unencrypted http. |
All metadata aggregates are signed using the same metadata signing key and the SHA-256 digest algorithm. To verify the signature on an aggregate, a consumer must obtain an authentic copy of the InCommon Metadata Signing Certificate.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| The IdP-only Aggregate is for SP deployments only! |
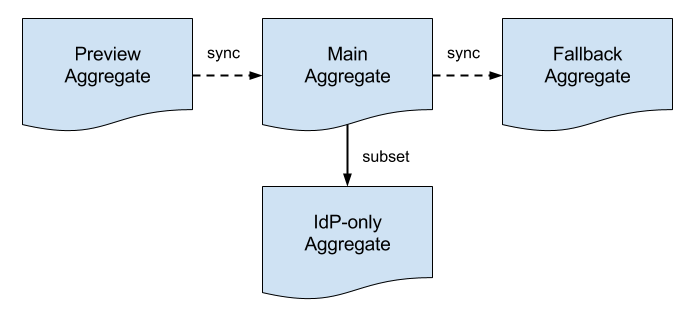
Operationally, structural changes to metadata are first introduced into the Preview Aggregate and subsequently synchronized with the Main Aggregate and the Fallback Aggregate, in that order. Time between synchronization events depends on the nature of the structural change.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Differences between the various metadata aggregates are recorded and archived daily:
The vertical diff captures changes to metadata over time. The horizontal diffs record the flow of metadata through the preview-main-fallback pipeline. |
Multiple metadata aggregates allows InCommon to deploy changes to metadata more quickly, easily, and safely. Metadata consumers choose exactly one of the three aggregates in the pipeline depending on the immediate requirements of their deployment.
| Advanced Tables - Table Plus | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
Multiple metadata aggregates allow InCommon to deploy changes to metadata more quickly, easily, and safely.
Preview Metadata Aggregate
The Preview Metadata Aggregate helps manage the introduction of potentially breaking changes into InCommon metadata. Before such a change is deployed to the Main Aggregate, it is first introduced in preview mode. Any issues that surface are addressed before the change is synced with the Main Aggregate.
The Preview Aggregate is designed for deployments on the leading edge, such as test and dev deployments. Such deployments are strongly encouraged to consume the Preview Aggregate instead of the Main Aggregate.
| Tip | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
An important decision point for each deployment is whether to consume the Main Aggregate or the Preview Aggregate. |
Main Metadata Aggregate
In the best possible world, a deployment would configure itself to refresh its metadata store from the production metadata aggregate Main Metadata Aggregate and that would be the end of it. The problem is that metadata aggregates are brittle by their very nature, that is, a small change to metadata may have unexpected effects downstream. If this happens, a deployment can “fall back” to a previous version of metadata that is known to be backward compatible.
...
As suggested in the previous section, the fallback metadata aggregate Fallback Metadata Aggregate comes into play when a breaking change is inadvertently introduced into InCommon metadata. When a change is made to the production metadata aggregateMain Aggregate, and that change breaks a downstream metadata process, an affected deployment can temporarily migrate to the fallback metadata aggregateFallback Aggregate. This gives the deployment time to adjust to the breaking change.
| Tip | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
A deployment should consume the Fallback Aggregate only when it has to, that is, when it is unable to consume the Main Aggregate. Consuming the Fallback Aggregate is a temporary measure while a deployment reacts to a breaking change introduced into InCommon metadata. See the article Using the Fallback Aggregate for more information. |
The fallback metadata aggregate Fallback Aggregate is transient in the sense that backward compatibility is provided for a limited, predetermined period of time. This forces deployments to adjust to breaking changes to production metadata albeit in a controlled environment.
Preview Metadata Aggregate
Like the fallback metadata aggregate, the preview metadata aggregate helps manage the introduction of potentially breaking changes into InCommon metadata. Before such a change is deployed in production, it is first introduced in preview mode. Any issues that surface are addressed before the change is moved to production.
The preview metadata aggregate is designed for deployments on the leading edge, such as test and dev deployments. Such deployments are strongly encouraged to consume the preview metadata aggregate instead of the production metadata aggregate.
...
| title | Production or Preview? |
|---|
...
.