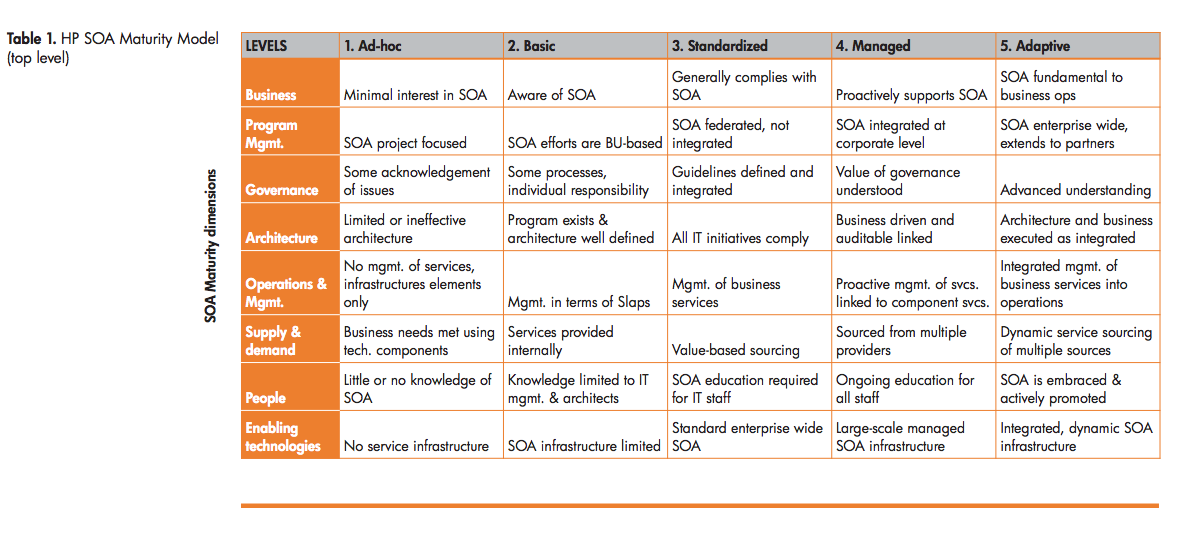
Organizational SOA maturity
Maturation (http://h71028.www7.hp.com/ERC/downloads/4AA0-4824ENW.pdf)
Message styles.
SOAP, REST and POX messages have different structures and syntax. However, the differences goes much deeper than that and affect the whole design of a system. REST builds on the fundamental concepts of HTTP and there are essentially two methods (GET and PUT). SOAP, by contrast, grew out earlier remote object technologies (such as CORBA and DCOM) and so it attempts to model remote object interactions. You can specify the equivalent of method names and input and output parameters.
1. SOA maturity of your organization
4. Governance
Describe governance structures that support SOA. Is this governance enterprise-wide or distributed.
- Inventory Management (service inventory). Publication of contracts. Is there an enterprise wide process for managing this?
- Do you have processes for documenting and publishing the services
- Do you have processes for managing changes to the services (change management)
- Is there any gate keeping over the publication of services (assuming you have an overall SOA for your enterprise)
- Data Governance. Successful SOA and successful data management go together?
- Have you developed a conceptual enterprise data model (or parts of one) ?
- Do you have data stewards. Do data stewards contribute to the definition of services?
- Is there an MDM (master data management) strategy?
- How does this connect to service message structures?
- Has SOA changed your IT governance? If so how?
- Has SOA introduced new roles and/or responsibilities?
5. Cost benefit analysis
- Metrics
- Cost to build each service
- Integration costs related to service re-use
- service reuse opportunities
- Strategic Value -- ROI
- Have processes been improved?
- Have new capabilities been provided?
- What other benefits have resulted from SOA, e.g., reusabile services reduced development time better access to enterprise data rationalization of business process?
6. SOA styles
- Message styles (notes). Different message styles are appropriate for different contexts. Which ones do you use?
- SOAP
- REST
- Plain old XML (POX)
- Other
- Design approach. How do you design your contracts?
- Contract first
- Bottom up (java annotations)
- Documentation. How do you document your service contracts?
- Interfaces published in javadoc
- XML schema
- Textual descriptions on wikis
- How do you mange trust between the various components
- If some components are in the cloud, how will that affect your security architecture
- Messaging: synch/asynch
7. Technologies
- Is a commercial "turnkey" SOA solution being used:
- Oracle fusion
- IBM websphere
- Are any open source or open source plus support solutions being used:
- MuleSoft
- WSO2
- Fuse
- Apache ServiceMix
- Has SOA led you to re-engineer your infrastructure? For example, if your data warehouse is the current hub of data exchange, does SOA change this?
8. Individual SOA projects and initiatives:
List up to three projects. Distinguish between SOA projects and projects that involve SOA. Where do these fall in the SOA maturation. Top-down or bottom-up. What business processes are being supported. How does this project move you forward in the maturity model. Does not have to be a technology project? SizrWhat are the goals of the project? Quantification. Can we make generalizations about where there is the most activity?
- Where they fall on the project lifecycle:
- Investigation
- Planning
- Execution
- Review
- What were the goals (business and technology)
- What business domains are addressed by this project:
- Learning tools ecosystem
- Learningt objects
- e-Portfolio
- Administrative systems
- Student (recruitment, admissions, academic records, registration, awards and financial aid, degree audit, advising)
- HR (recruitment, benefits, payroll, pension, leaves)
- Finance
- Research (grant applications, ethics, funding, publications)
- Publications
- Learning tools ecosystem
- Enterprise infrastructure
- Workflow
- Other (please describe)